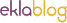-
Vista Ie View Settings
Windows, Office, Xbox & More. For printers, cameras, network cards, and more.
Windows, Office, Xbox & More. For printers, cameras, network cards, and more.

Original title: Error message when downloading iTunes and Norton Internet Security I got an error message when downloading iTunes that said my current security.
InformationWeek shares news, analysis and advice on operating systems, from Microsoft Windows 8 to Apple iOS 7. ETrex 30x is our upgraded version of the popular eTrex 30, with enhanced screen resolution for a more readable display and internal memory expanded to hold more maps. Get help, support, and tutorials for Windows products—Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, and Windows 10 Mobile. Advanced Security IE Settings in a GPO. These same Advanced Security settings for IE are exposed to many versions of IE through the use of Group Policy.
Configuring Advanced IE Settings Using Group Policy. Introduction. There is no question, especially after the last month of IE scares, that every computer running Internet Explorer needs to be locked down and secured. With many advances from Microsoft within IE, such as UAC, Protected Mode, Integrity levels, and more, there still seems to be some incorrect configurations of IE.
Not only incorrect configurations, but after my last tour of speaking on Windows security throughout the United States, there still seems to be some confusion regarding the Advanced Security settings that are available within IE. In this article I will go over what the Advanced Security settings mean and give some direction on how best to configure each. Where to Find the Advanced Security Settings. There might be some confusion as to which IE security settings I am referring to, so let me be clear about this. The security settings I am referring to are under the Tools – Internet Options menu within IE. Once you get the Internet Options dialog box open, you then click on the Advanced tab.
Under the Advanced tab, you scroll down until you see the Security section, which can be seen in Figure 1. Figure 1: The Advanced Security settings section for Internet Explorer. It is this suite of settings that I am referring to for this article. Advanced Security IE Settings in a GPOThese same Advanced Security settings for IE are exposed to many versions of IE through the use of Group Policy.
The versions of IE that are supported include: 5, 6, 7, and 8. For you to access these Advanced Security IE settings using a GPO, you will need to have the Group Policy Preferences (GPP) available to you. You must be using Windows Server 2. Vista SP1, 7, or Windows Server 2.
R2 to see the GPP. For more information on obtaining GPP, check out this article on Window. Security. com. Once you have the correct version of the GPMC installed in order to view the GPP, you will then need to get to the correct policy to setup the Advanced Security settings. To get to this policy, you will go to User Configuration\Preferences\Control Panel Settings\Internet Explorer. From this location you can add in policies for all the appropriate versions of IE. Specific Security Settings Allow active content from CDs to run on my computer. Active content includes Active.
X controls and web browser add- ons used by many Internet Web sites. These programs are typically blocked because they can malfunction or attackers can perform tasks on your computer without your knowledge. Default: Not checked. Recommended: Not checked. Allow active content to run in files on my computer. Same as last setting, except from files instead of from a CD. Default: Not checked.
Recommended: Not checked. Allow software to run or install even if the signature is invalid.
Signatures can be associated with specific applications and installations, tying them back to the manufacturer. This helps keep the application or installation “true” and helps you determine if the application or installation is a fake. Default: Not checked.
Recommended: Not checked. Check for publisher’s certificate revocation. Often a certificate needs to be revoked due to a compromised private key or the certificate has expired. This setting will first check for the certificate on the revocation list before it allows it to be used. Certificates are Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked.
Check for server certificate revocation. Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked. Check for signatures on downloaded programs. Often a certificate needs to be revoked due to a compromised private key or the certificate has expired. This setting will first check for the certificate on the revocation list before it allows it to be used.
Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked.
Do not save encrypted pages to disk. If data from an HTTPS Web site connection is saved to your disk, this might pose a potential attacker to access the data via the saved data in the Temporary Internet folder. Of course, it is more efficient and faster to save this data to the disk for future access to the Web site. Not saving this encrypted data is more secure than allowing it to be saved. Default: Not checked.
Recommended: Checked. Empty temporary files folder when browser is closed. The temporary files folder for IE stores a lot of data from each site that you visit. This information is cached on your disk for faster access the next time you visit that site. However, worms, viruses, and other malicious software can be stored along with the good Web site data. Therefore, clearing out the files on a regular basis is a more secure configuration than allowing it to be stored.
Default: Not checked. Recommended: Checked. Enable DOM storage. DOM (Document Object Model) Storage is designed to provide a larger, securer, and easier- to- use alternative to storing information in cookies. DOM is used for programs like Java. Script to provide dynamic websites and deliver customized web pages for users.
This behavior should not be allowed unless DOM storage is necessary for the business task on the Internet. Default: Checked. Recommended: Not Checked. Enable integrated windows authentication.
Forces IE to use Kerberos or NTLM for authentication, instead of using anonymous, Basic authentication, or Digest. Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked.
Enable memory protection to help mitigate online attacks. This controls whether or not IE uses DEP (Data Execution Protection), which helps protect your computer from ill- behaving applications that could harm your computer. Default: Not Checked.
Recommended: Checked. Enable native xmlhttp support. Used by many companies as a standard today to provide dynamic control over data via many Web sites.
Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked. Phishing Filter. Phishing Filter interrupts the ability to navigate to and download from sites known to host malicious content. It also helps you avoid socially engineered malware phishing Web sites and potential online fraud. The filter will check the Web site against a list of or reported phishing sites, check software downloads against a list of reported malicious software, and helps prevent you from visiting sites that might lead to identity theft. The encryption is based on a certificate that provides Internet Explorer with the information it needs to communicate securely with the website.
Certificates also identify the website and owner or company. Default: Not checked. Recommended: Not checked. Use ssl 3. 0. Same as Use SSL 2. SSLDefault: Checked.
Recommended: Checked. Use tls 1. 0. TLS (Transport Layer Security) 1. SSL Web sites to protect and encrypt the data and connection. Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked. Use tls 1. 1. TLS (Transport Layer Security) 1.
SSL Web sites to protect and encrypt the data and connection. Enable only if you know the Web site supports this version of TLS. Default: Not checked. Recommended: Not checked. Use tls 1. 2. TLS (Transport Layer Security) 1. SSL Web sites to protect and encrypt the data and connection. Enable only if you know the Web site supports this version of TLS.
Default: Not checked. Recommended: Not checked. Warn about certificate address mismatch. Provides warnings when the certificate for a Web site is not matching the Web site for which it is being used. Default: Checked.
Recommended: Checked. Warn if changing between secure and not secure mode.
If a Web site has a mixture of HTTP and HTTPS links, or you are being sent from an HTTPS site to a non- secure, HTTP, site, you will be warned. Default: Not checked. Recommended: Checked.
Warn if POST submittal is redirected to a zone that does not permit posts. Warns if you are working on a form on the Internet that redirects you to an address that is different from the one that is hosting the form. This will help prevent your information or browser from being redirected to a non- secure site.
Default: Checked. Recommended: Checked. Summary. The Advanced Security settings for IE are very detailed and can help protect desktops and the entire network from attacks and vulnerabilities. Using them correctly can make all the difference from a more secured computer and one that is not very secure at all. The ability to leverage Group Policy to configure these settings for versions 5, 6, 7, and 8 of IE makes the solution effective and efficient.
-
Commentaires